Sawn timber manufacturing is a highly automated process. It proceeds in the order of the the process. This section first introduces the production planning of sawmills.
After sorting and measuring the log, the actual sawing process begins. Process begins with peeling and continues with demonstration of sawing techniques, sawing machines, saw lines, by-product handling and blade technology. This is followed by fresh sorting, ribbing, drying, dry sorting and packing of lumber. Process automation in sawmills, in-line measurements, and machine vision applications used in sawn timber quality will complete this extensive chapter.
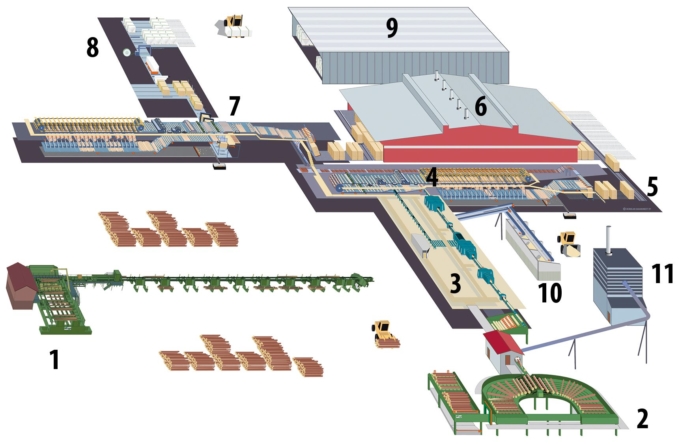
Principles:
- The sawing process starts at the timber sorting line and log storage (1).
- The logs travel towards the sawing machine through a debarker (2).
- The actual sawing line, where the log is turned into sawn goods, is located in the sawing plant. (3).
- The freshly sawn timber is taken directly to the dimension sorting plant, i.e. the green sorting plant (4). From there the timber is taken to the stick-stacking station to be stacked into drying loads (5).
- Drying takes place in the chamber and progressive kilns (6).
- Dry sawn timber is sorted at the sorting plant into its final grades. (7).
- The sawn goods are then packaged in the packaging line for delivery to the customers (8).
- The packages are transferred into storage to wait for their dispatch and transport (9).
- By-products of the sawing process, such as chips and sawdust, are transferred from the chipper through a screen into silos (10).
- There is also a heating plant operating in connection to the sawmill. The heating plant uses the removed bark as its main source of fuel (11).