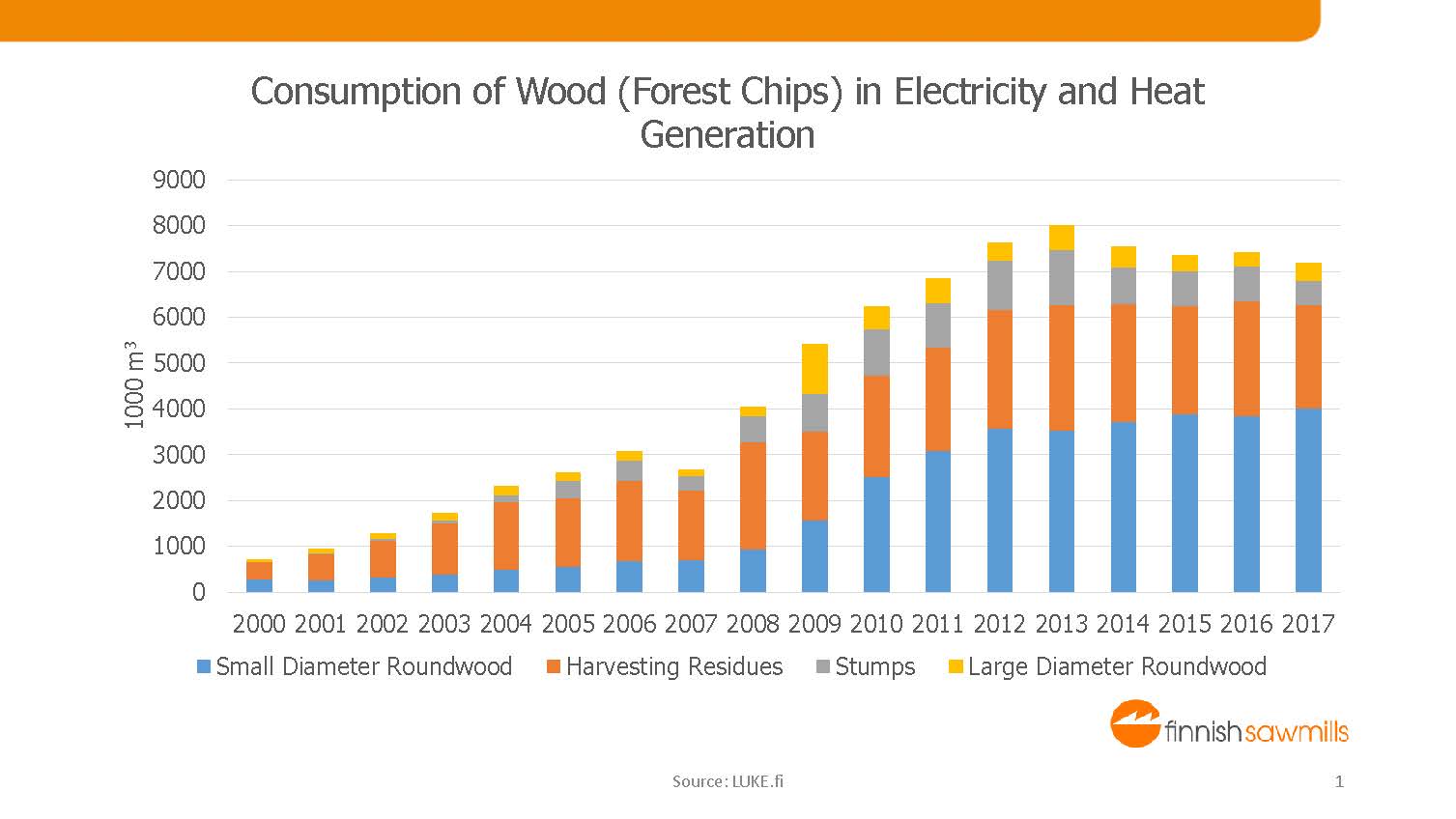
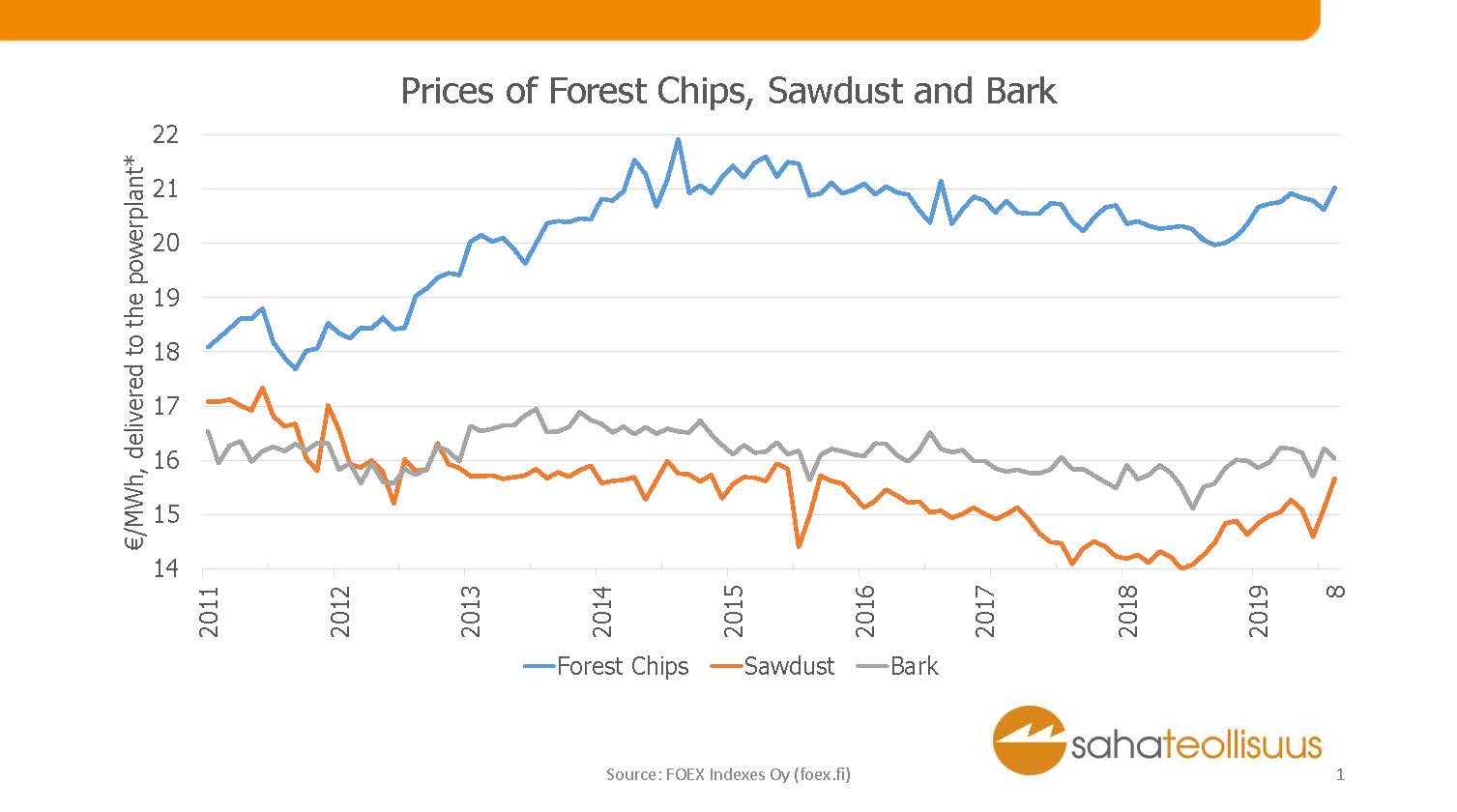
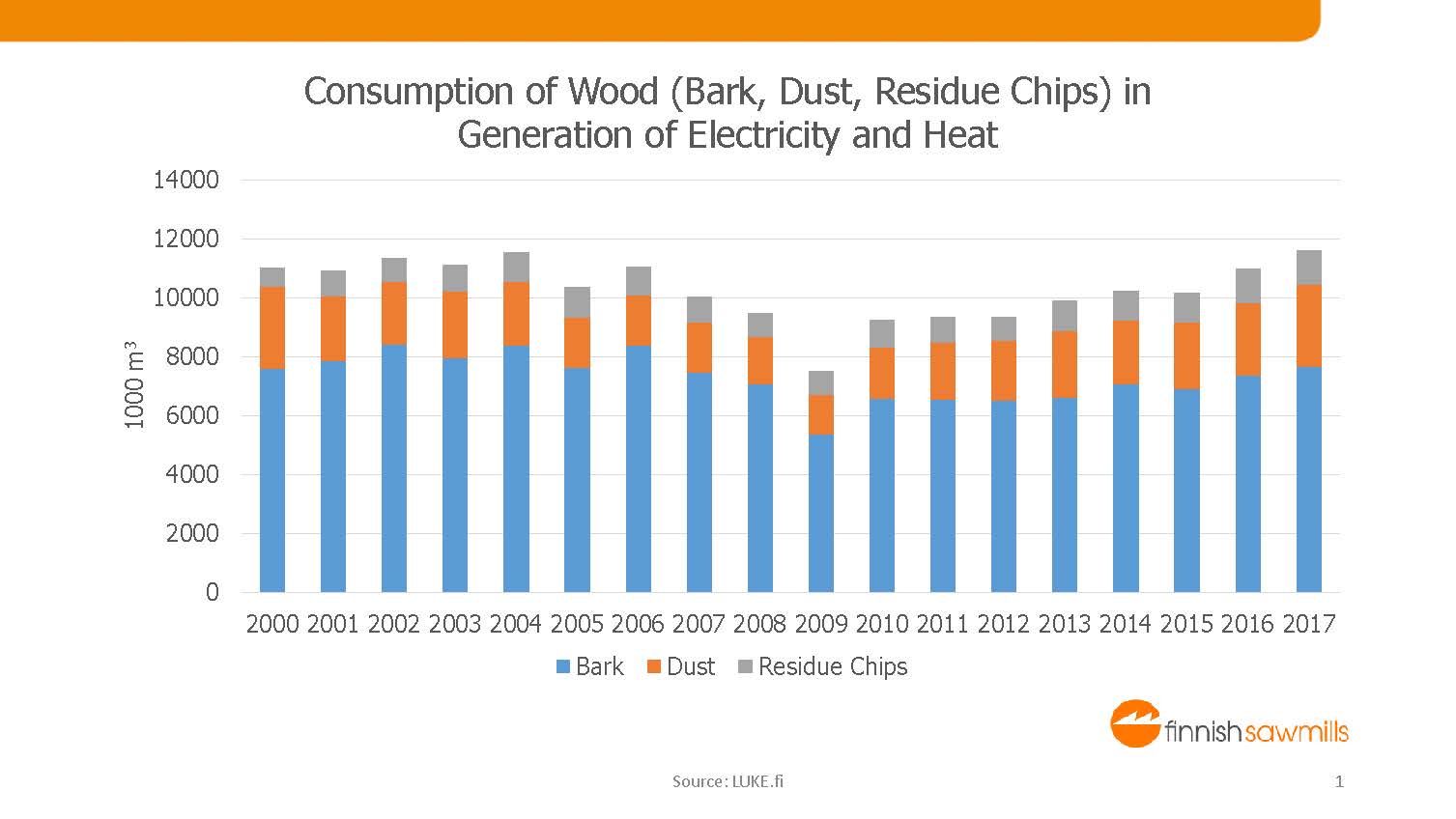
The meaning of the sawmilling industry in solid biofuel production is significant. Over half of the raw material for wood chips originates as a by-product from the raw material procurement of sawmills.
Additionally, it is noticeable that sawmills themselves are significant producers of combustible residues, bark and sawdust.
The production process of sawmills is energy self-sufficient. A sawmill produces more energy than it consumes.
Energy balance at the sawmills
One cubic meter of logs produces
- about 50 % timber
- about 30 % high grade polo chips
- about 10 % sawdust
- about 10 % bark.
From the bark and the sawdust about a third is needed at the sawmill for the production of thermal energy to kiln dry the timber and, the rest is sold either as raw material for wood-based panel industry, chemical forest industry, or as fuel for energy or biofuel producers.
A 10MW heat generating boiler at a medium sized sawmill (production 250,000 m3 per year) could be replaced with a power plant with about a 3 to 5MW turbine, which could produce the thermal energy necessary to the run the sawmill as well as a significant amount of electricity. This kind of de-centralised CHP (Combined Heat and Power) generation could back the governments renewable energy policy, amount other things by offering e.g. required adjusting power for wind power generators.
There are only four CHP plants within the Finnish sawmilling industry which were built with the support of the previous investment aid.